Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a common issue that affects many men, and a variety of factors, including restricted blood flow or nerve damage, can cause it. It can make it difficult to achieve or maintain an erection that is firm enough for sensual activity, and it is important to seek treatment for this condition. ED impacts more than 40 million men. Fortunately, treatments available can help improve sensual health and overall well-being.
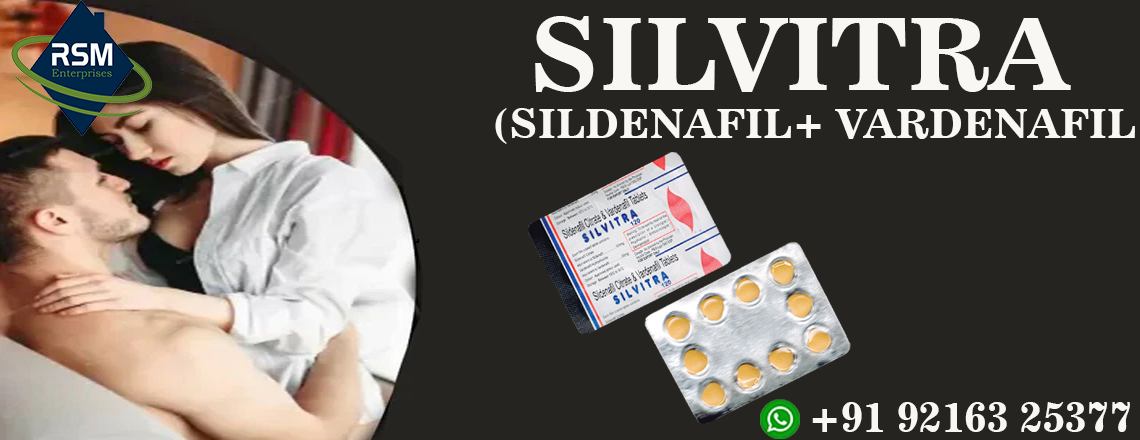
One such treatment option is Silvitra 120, an oral medication specifically designed to address erection problems during sensual intimacy. Silvitra 120mg contains two active ingredients, Sildenafil Citrate 100mg and Vardenafil 20mg, which increase blood flow to the genital part and promote stronger and longer-lasting erections. It is important to note that Silvitra 120 should only be taken under the guidance and supervision of a qualified healthcare professional. It is also important to remember that maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help improve erectile function and overall sensual health.
How Silvitra 120 Works
Silvitra 120mg works by increasing blood flow to the genital part, which helps to produce and maintain an erection. Both sildenafil 100mg and vardenafil 20mg are PDE5 inhibitors, which means they work by blocking the enzyme that regulates blood flow to the genital part. By inhibiting this enzyme, these medications help to relax the blood vessels in the genital part, allowing more blood to flow in and produce an erection. However, it is important to note that sensual stimulation is still required to achieve an erection. Silvitra 120mg does not work without sensual stimulation.
Benefits of Silvitra 120
Silvitra 120mg offers several benefits for men with ED. First and foremost, it is a highly effective treatment option. In clinical trials, Silvitra 120 has been shown to improve erectile function significantly. It is effective in men with a wide range of underlying causes of ED, including diabetes, high blood pressure, and prostate surgery.
Another benefit of Silvitra 120mg is its ease of use. Unlike other treatment options for ED, such as injections or penile implants, Silvitra 120 is taken orally. It makes it a more convenient and discreet treatment option.
Additionally, Silvitra 120mg is generally well-tolerated, with few side effects. Usual side effects retain headache, facial flushing, and indigestion. These side effects are generally benign and go away within a few hours. Serious side effects are rare, but men should seek medical attention immediately if they experience chest pain, dizziness, or vision changes.
Finally, Silvitra 120 is a cost-effective treatment option. It is less expensive than some other ED medications, making it a more affordable option for men needing ongoing ED treatment.
Dosage and Administration
The recommended dosage for Silvitra 120 is one tablet taken orally, 30 minutes to 1 hour before sensual activity. The tablet should be taken with a glass of water and with or without food. It is important to note that Silvitra 120mg should not be taken more than once daily.
It is also important to follow the instructions provided by your healthcare provider when taking Silvitra 120mg. Your healthcare provider will advise you on the appropriate dosage and frequency of use based on your needs and medical history.
Precautions and Contraindications
Like all medications, Silvitra 120mg is not suitable for everyone. Men with certain medical conditions, such as severe liver or kidney disease, should not take this medication. Additionally, men taking nitrates, such as nitroglycerin, should not take Silvitra 120mg for chest pain. Integrating these pills can induce a dangerous fall in blood pressure.
Men taking alpha-blockers for high blood pressure should also use caution when taking Silvitra 120. Combining these medications can cause a drop in blood pressure, leading to dizziness or fainting.
Men with a history of heart attack or stroke should also use caution when taking Silvitra 120. This medication can increase the risk of these events in men with underlying cardiovascular disease.
 Visit our USFDA APPROVED Spices Division
Visit our USFDA APPROVED Spices Division